MO412 1s2023 - Fillipi Valadares
mathJax
Friday, June 2, 2023
7th Quiz - 02/06/2023
Thursday, May 18, 2023
6th quiz - 19/05/2023
- The Power Grid network is neutral, since the degree correlation of real and randomized data are indistinguishable;
- The Metabolic network presents structural disassortativity, rooted in the scale free nature of the network;
- The Actor network is assortative, noticed by ascending and indistinguishable real and randomized degree correlations;
- A possible way to make the Metabolic network neutral or assortative, would be by removing all hubs with degrees larget than the structural cutoff (\(k_{s}\));
- None of the above.
Friday, May 5, 2023
5th quiz - 05/05/2023
Given the following directed graph, if we executed Kosaraju-Sharir’s algorithm to detect the strongly connected components (SCCs) starting at node A and using descending DFS ordenation (Z to A), what would the SCCs be and in which order they would be returned?
- 2 SCCs: returned first BDCA and last FGH;
- 2 SCCs: returned first FGH and last BDCA;
- 4 SCCs: returned first H, G, F and last BDCA;
- 4 SCCs: returned first BDCA, F, G and last H;
- None of the above.
Friday, March 31, 2023
3rd Quiz - 31/03/23
Generally Real Networks do not behave according to the Random Networks Model, even so, they can share some properties. Analyse the following statements.
- The degree distribution of a network can be closely aproximated as a Poisson distribution;
- At \(\left \langle k \right \rangle\) > 1, it exists a giant component in the network;
- Average path length can be predicted as \(\left \langle d \right \rangle = \frac{ln N}{ln \left \langle k \right \rangle}\) and can present Small World property;
- The average clustering coefficient \(\left \langle c \right \rangle\) generally appears to be independent of the number of nodes N.
Which option contains the true statements for Random Networks that can be found also in general Real Networks?
- I and IV;
- II and III;
- II and IV;
- I, II and III;
- None of the above.
Friday, March 17, 2023
2nd Quiz - 17/03/23
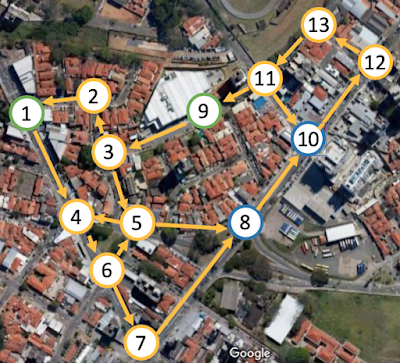
Given the image bellow of a small part of the Campinas' streets represented in a graph and your knowledge about Network Science, check the following affirmations.
- There is only one shortest path between nodes 1 and 9 and it has length 9;
- The given graph is strongly connected;
- A shortest path can contain a loop;
- If we executed BFS Algorithm starting at node 9, the longest distance would be 7;
- The link between nodes 8 and 10 is a bridge (bridge as the Network Science definition).
Select the answer with only the true affirmations:
- I, II and V;
- I, III and IV;
- II and IV;
- II, IV and V;
- None of the above.
Thursday, March 9, 2023
1st Quiz - 10/03/23
Given the unweighted directed graph bellow:
What are the values for incoming and outgoing degree's of node 4, and what is the average degree of the network?
- \(k_{4}^{in}\) = 1, \(k_{4}^{out}\) = 3, \( \left \langle k \right \rangle \) = \(\frac{6}{7}\);
- \(k_{4}^{in}\) = 1, \(k_{4}^{out}\) = 3, \( \left \langle k \right \rangle \) = \(\frac{7}{6}\);
- \(k_{4}^{in}\) = 3, \(k_{4}^{out}\) = 1, \( \left \langle k \right \rangle \) = \(\frac{6}{7}\);
- \(k_{4}^{in}\) = 3, \(k_{4}^{out}\) = 1, \( \left \langle k \right \rangle \) = \(\frac{7}{6}\);
- None of the above.
7th Quiz - 02/06/2023
Agglomerative hierarchical clustering can be applied to community detection in graphs. By using dendrograms, one can visualize the order in ...

-
Agglomerative hierarchical clustering can be applied to community detection in graphs. By using dendrograms, one can visualize the order in ...
-
Generally Real Networks do not behave according to the Random Networks Model, even so, they can share some properties. Analyse the followin...
-
Given the image bellow of a small part of the Campinas' streets represented in a graph and your knowledge about Network Science, check t...